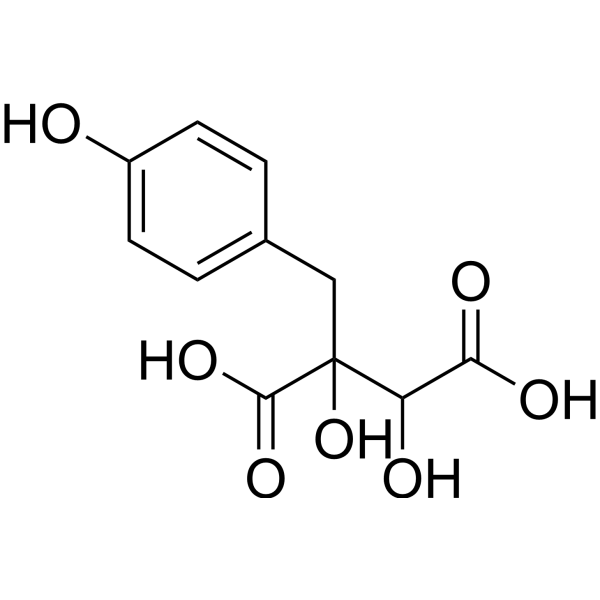
Piscidic acid
CAS No. 469-65-8
Piscidic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M32380 CAS No. 469-65-8
Piscidic acid acts as an inhibitor of cholesterol permeation through Caco-2 cell monolayers and as an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 421 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePiscidic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPiscidic acid acts as an inhibitor of cholesterol permeation through Caco-2 cell monolayers and as an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase.
-
DescriptionPiscidic acid acts as an inhibitor of cholesterol permeation through Caco-2 cell monolayers and as an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase. Piscidic acid have antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number469-65-8
-
Formula Weight256.21
-
Molecular FormulaC11H12O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO, Pyridine, Methanol, Ethanol, etc.
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Arch Pharm Res . 2017 Nov;40(11):1278-1286.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Flavanomarein
Flavanomarein demonstrates potent antioxidative property, including free radical scavenging activity, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, as well as lipid-lowering effects in human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells treated with free fatty acids (FFAs).
-
Etretinate
Etretinate is a RAR and RXR agonist previoulsy used to treat psoriasis. It induces brth defects and suppresses proliferation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma models.
-
Naringenin triacetat...
Naringenin triacetate exhibits a better binding affinity with multiple crystal structures of first bromodomain BRD4 (BRD4 BD1) when compared with the known inhibitors.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


